ZStack Cloud Platform
Single Server, Free Trial for One Year

Rapid business growth requires large-scale computing, storage, and other resources, but these resources cannot be fully utilized and their potential efficiency cannot be realized in the data center, resulting in a dual waste of resources and funds.

The rapid changes in internet services, along with technology or application architecture upgrades, can exert significant pressure on the infrastructure layer. Operations such as hardware expansion and network transformation are complex and can impact business operations.

In cloud computing applications, product iterations and upgrades occur rapidly, and there are numerous development and testing environments. IT needs to respond promptly to the demands of product development and testing, which traditional resource management methods simply cannot meet.
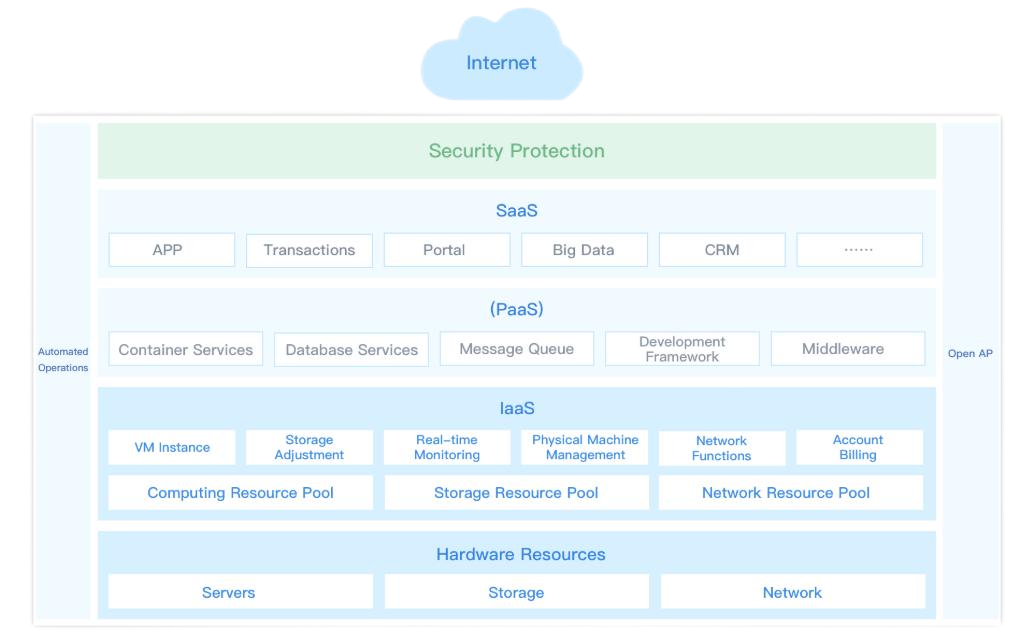

Cloud platforms can fully utilize existing server resources and also interface with centralized storage. This not only protects existing IT resource investments but also reduces the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Cloud platforms support productized deployment with an intelligent UI guide, allowing users to complete setup within 30 minutes without complex configurations or specialized skills. Additionally, the platform features automatic monitoring and alert capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring of the cloud platform’s operational status.

Open API interfaces enable business applications to quickly integrate with cloud infrastructure, helping users build an integrated data application system from applications to infrastructure.
Cloud platforms support elastic scaling, automatically adjusting resource configurations based on load conditions. This increases resources during peak periods to meet demand and reduces resources during low load periods to save costs.